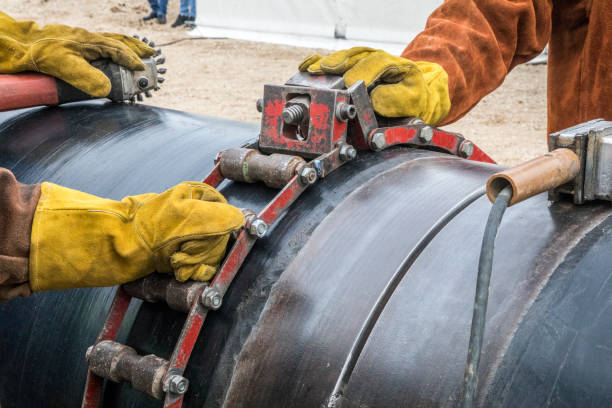
Pipe clamps, also known as pipe vises or pipe clamps, are versatile tools used to securely hold pipes, tubes, or cylindrical objects in place during various construction, plumbing, or repair tasks. These clamps consist of two serrated jaws or pads that can be adjusted to grip pipes of different diameters firmly.
Pipe clamps are available in various types, including:
- C-Clamps: These clamps feature a C-shaped frame with an adjustable screw that tightens the jaws around the pipe. C-clamps are commonly used for light-duty applications and are available in different sizes to accommodate different pipe diameters.
- Hinged Pipe Clamps: These clamps have a hinged design that allows the jaws to open wide, making it easier to position the clamp around the pipe. Hinged pipe clamps often have a quick-release mechanism for easy adjustments.
- Chain Pipe Clamps: As the name suggests, these clamps use a chain or cable to wrap around the pipe, providing a secure grip. Chain pipe clamps are ideal for larger pipes or irregular shapes and can be adjusted to fit various diameters.
Pipe clamps are typically made from durable materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum alloys to withstand the demands of heavy-duty applications. The jaws or pads are often coated with a non-slip material, such as rubber or plastic, to prevent marring or damaging the surface of the pipe.
Table of Contents
Uses of Pipe Clamps
Pipe clamps are versatile tools that find applications in various industries and projects, particularly in woodworking, metalworking, construction, and DIY endeavors. Their ability to apply consistent clamping pressure makes them invaluable for securing materials during assembly, gluing, welding, or other processes.
Woodworking
In woodworking, pipe clamps are essential for gluing and clamping wood pieces together, such as when creating furniture, cabinets, or other wooden structures. They ensure a tight and even bond between the components, allowing the adhesive to cure properly. Pipe clamps can also be used for temporarily holding workpieces in place during cutting, routing, or other operations.
Metalworking
In metalworking, pipe clamps play a crucial role in welding and fabrication projects. They are used to hold metal components securely in position during welding, preventing warping or misalignment. Pipe clamps can also be employed for clamping metal pieces together for drilling, cutting, or other metalworking processes.
Construction
In construction settings, pipe clamps are commonly used for temporarily securing formwork, bracing, or other structural elements during concrete pouring or framing operations. Their adjustable nature allows them to accommodate various sizes and shapes, ensuring a tight and secure fit.
DIY Projects
For DIY enthusiasts, pipe clamps are indispensable tools for a wide range of projects, from woodworking and metalworking to home improvement tasks. They can be used for clamping materials during painting, staining, or varnishing, as well as for holding components in place during assembly or repair work.
Overall, the versatility and clamping power of pipe clamps make them invaluable tools for professionals and hobbyists alike, enabling precise and secure workpiece positioning across various applications.
How to Use Pipe Clamps
Using pipe clamps is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to follow the proper steps and safety precautions to ensure a secure and effective clamping setup. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use pipe clamps:
- Prepare the Work Area: Clear the work area and ensure you have enough space to maneuver the pipe clamps and the materials you’ll be clamping.
- Select the Appropriate Pipe Clamp: Choose a pipe clamp that is suitable for the size and weight of the materials you’ll be clamping. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the clamp’s capacity and recommended usage.
- Inspect the Pipe Clamp: Before using the pipe clamp, inspect it for any signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or missing parts. Ensure that the threads on the clamp and the pipe are in good condition and free from debris.
- Assemble the Pipe Clamp: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to properly assemble the pipe clamp. This typically involves attaching the clamp head to the pipe and tightening the necessary components.
- Position the Pipe Clamp: Place the pipe clamp in the desired location, ensuring that it is stable and secure. If clamping multiple pieces, position the clamps evenly along the materials.
- Apply Clamping Pressure: Gradually tighten the clamp by turning the adjustment mechanism, such as a screw or lever. Apply enough pressure to hold the materials securely, but avoid over-tightening, which could damage the materials or the clamp itself.
- Check for Proper Clamping: Once the clamp is tightened, check that the materials are securely held in place and that there is no movement or shifting.
- Perform the Desired Task: With the materials securely clamped, you can now proceed with your desired task, such as welding, gluing, or cutting.
- Release the Clamp: After completing the task, gradually release the clamping pressure by loosening the adjustment mechanism. Be cautious, as the materials may shift or move once the clamp is released.
- Clean and Store the Pipe Clamp: After use, clean the pipe clamp to remove any debris or residue. Store the clamp in a dry, protected area to prevent damage or corrosion.
Safety Precautions:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing, when using pipe clamps.
- Ensure that the pipe clamp is rated for the weight and size of the materials you’re clamping.
- Never exceed the clamp’s maximum clamping capacity.
- Be cautious when tightening or releasing the clamp, as the materials may shift or move unexpectedly.
- Keep your hands and other body parts clear of the clamping area to avoid pinching or crushing injuries.
Tips and Tricks:
- Use clamp pads or protective materials between the clamp and the workpiece to prevent surface damage or marring.
- For irregular or curved surfaces, use clamps with adjustable or swiveling heads for better clamping versatility.
- Consider using multiple clamps for larger or heavier materials to distribute the clamping force evenly.
- Periodically check the tightness of the clamp during use, as materials may shift or settle over time.
By following these step-by-step instructions, safety precautions, and tips, you can effectively and safely use pipe clamps for a wide range of applications, ensuring a secure hold and successful project completion.
Types of Pipe Clamps
Pipe clamps come in various shapes and designs, each suited for specific applications and materials. Here are some of the most common types:
Rebar Clamps: These clamps are designed to grip and hold reinforcing bars (rebar) used in concrete construction. They feature serrated jaws that securely grip the rebar, allowing workers to position and align the bars during the concrete pouring process.
Corner Clamps: As the name suggests, corner clamps are used to join two pieces of material at a 90-degree angle, such as when assembling frames or structures. They typically have two swiveling jaws that can be adjusted to accommodate different material thicknesses.
C-Clamps: C-clamps are versatile and commonly used for a wide range of clamping tasks. They consist of a C-shaped frame with a fixed jaw on one end and a movable jaw on the other, operated by a threaded screw or lever. C-clamps are available in various sizes and can be used to clamp materials together or to hold workpieces in place.
H-Clamps: H-clamps, also known as bar clamps or cabinet clamps, are designed for clamping long, flat surfaces together. They feature a horizontal bar that spans the width of the workpieces, with adjustable jaws at each end. H-clamps are commonly used in woodworking and cabinetry projects.
Pipe Clamp Variations: While the basic design of pipe clamps involves a threaded shaft and two clamping jaws, there are several variations to accommodate different materials and applications. Some examples include:
- Adjustable Pipe Clamps: These clamps have adjustable jaws that can be repositioned along the shaft, allowing for clamping at different angles or on irregular surfaces.
- Swivel Pipe Clamps: The clamping jaws on these clamps can rotate or swivel, making them suitable for clamping curved or angled surfaces.
- Deep Throat Pipe Clamps: These clamps have an extended throat depth, allowing them to clamp materials that are thicker or deeper than standard pipe clamps.
- Spring Pipe Clamps: Instead of a threaded shaft, these clamps use a spring-loaded mechanism to apply clamping force, providing quick and easy clamping and release.
Each type of pipe clamp is designed to meet specific clamping needs, whether it’s holding materials in place during construction, assembly, or woodworking projects. Choosing the right clamp for the job ensures a secure and efficient clamping solution.

Pipe Clamp Materials
Pipe clamps are typically made from durable and robust materials that can withstand the rigors of clamping and securing various objects. The choice of material plays a crucial role in determining the strength, durability, and weight of the clamp. Here are some common materials used in the construction of pipe clamps:
Steel: Steel is one of the most widely used materials for pipe clamps due to its exceptional strength and durability. Carbon steel and alloy steel are popular choices, offering high tensile strength and resistance to deformation under heavy loads. Steel pipe clamps can handle significant clamping forces and are suitable for demanding applications.
Aluminum: Aluminum pipe clamps are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern or in environments with moisture or chemical exposure. While not as strong as steel, aluminum clamps offer a good balance of strength and weight, making them a popular choice for various projects.
Cast Iron: Cast iron pipe clamps are known for their robustness and durability. They are often used in heavy-duty applications where immense clamping force is required. Cast iron clamps are resistant to deformation and can withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for industrial and construction settings.
Alloys: Manufacturers sometimes use specialized alloys to create pipe clamps with specific properties. For example, stainless steel alloys offer superior corrosion resistance, while titanium alloys provide high strength-to-weight ratios. These alloys are typically more expensive but can be advantageous in certain applications.
The strength and durability of pipe clamps are crucial factors to consider when selecting the material. Steel and cast iron clamps are generally the strongest, capable of withstanding high clamping forces and heavy loads. Aluminum clamps, while lighter, may have lower clamping capacities but offer excellent corrosion resistance. Ultimately, the choice of material depends on the intended use, desired strength, weight considerations, and environmental conditions in which the clamp will be used.
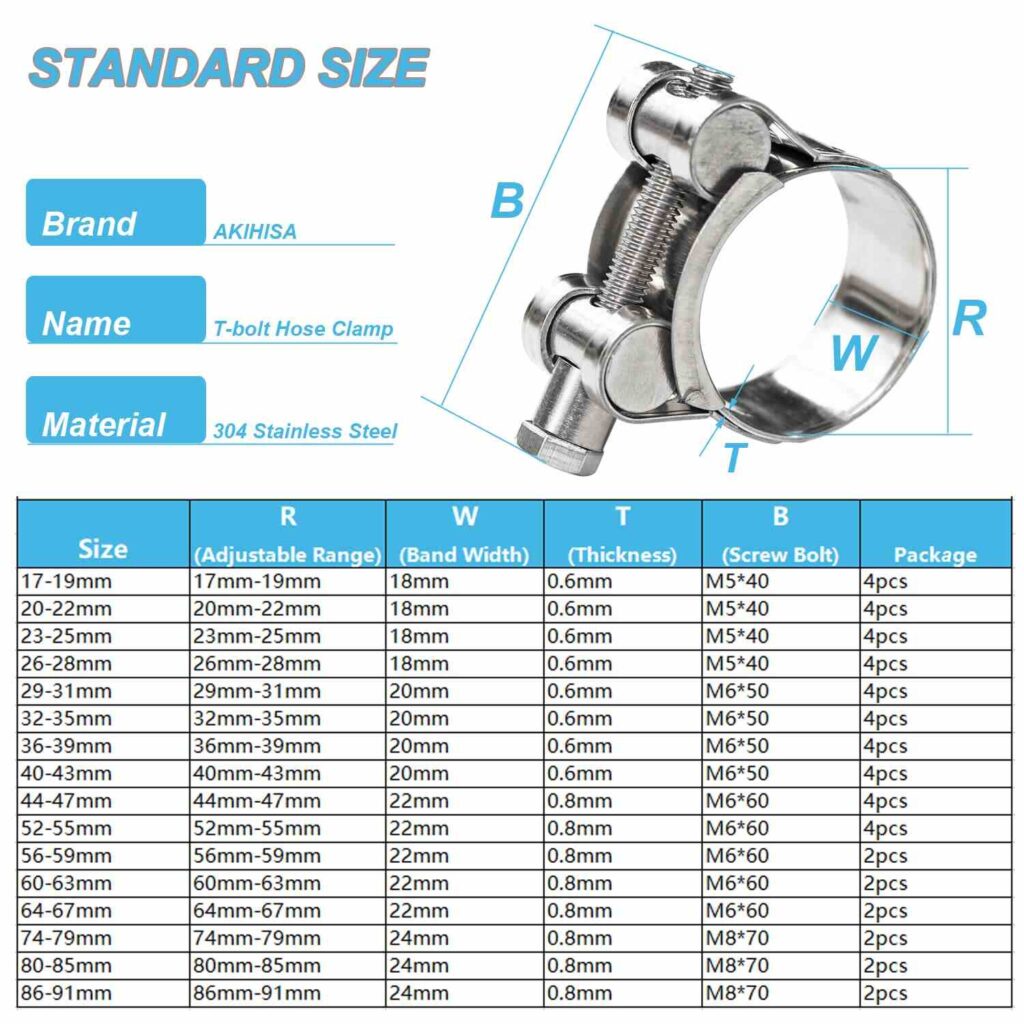
Pipe Clamp Sizes and Capacities
Pipe clamps come in a wide range of sizes and capacities to accommodate various pipe diameters and clamping requirements. The size of a pipe clamp is typically determined by the maximum outside diameter of the pipe it can securely grip.
Common Sizes:
- 1/2 inch to 4 inches: These smaller sizes are suitable for clamping copper, PVC, and other lightweight pipes used in plumbing, HVAC, and general construction projects.
- 4 inches to 8 inches: These mid-range sizes are commonly used for securing larger metal pipes, such as those found in industrial settings or heavy-duty construction projects.
- 8 inches to 24 inches: These larger sizes are designed for clamping heavy-duty pipes, such as those used in oil and gas pipelines, power plants, and other industrial applications.
Clamping Force and Pressure Ratings:
Pipe clamps are rated for the maximum clamping force they can exert, typically measured in pounds or tons. Higher clamping forces allow the clamp to securely grip pipes under greater pressure or stress. Pressure ratings indicate the maximum internal pressure the clamped pipe can withstand without slipping or failing.
Load-Bearing Capacities:
In addition to clamping force, pipe clamps are rated for their load-bearing capacity, which is the maximum weight or force they can support without failing or deforming. This rating is crucial when using pipe clamps for structural support or in situations where the clamped pipe will be subjected to significant loads or stresses.
It’s essential to select a pipe clamp with the appropriate size, clamping force, pressure rating, and load-bearing capacity for the specific application. Using an undersized or inadequately rated clamp can lead to pipe slippage, leaks, or even catastrophic failures, resulting in property damage, environmental hazards, or personal injury.
Choosing the Right Pipe Clamp
Selecting the appropriate pipe clamp is crucial for ensuring a secure hold and preventing potential accidents or damage. Several factors should be considered when choosing the right pipe clamp for your application.
Factors to Consider:
- Pipe Material and Diameter: Pipe clamps are designed to grip pipes of specific materials and diameters. Ensure that the clamp you choose is compatible with the pipe material (e.g., steel, copper, PVC) and can accommodate the pipe’s outer diameter.
- Clamping Force: Different pipe clamps offer varying clamping forces, measured in pounds or newtons. Determine the required clamping force based on the weight of the pipe and any additional loads it may need to support.
- Jaw Type: Pipe clamps come with different jaw types, such as smooth, serrated, or cushioned. Smooth jaws are suitable for softer materials like plastic or copper, while serrated jaws provide a better grip on harder materials like steel.
- Throat Depth: The throat depth refers to the maximum distance between the clamp’s jaws and the body. Ensure that the throat depth is sufficient to accommodate the pipe and any obstructions or fittings.
- Adjustability: Some pipe clamps offer adjustable features, such as swiveling heads or adjustable jaw positions, which can be beneficial for working in tight spaces or accommodating different pipe configurations.
Matching Clamps to Applications:
- Plumbing and Pipe Fitting: For plumbing and pipe fitting tasks, choose clamps with smooth or cushioned jaws to prevent damage to the pipe material. Consider adjustable clamps for added versatility.
- Welding and Fabrication: In welding and fabrication applications, serrated jaw clamps provide a secure grip on metal pipes, preventing slippage during the welding process.
- Temporary Support: For temporary pipe support or positioning, lightweight and adjustable clamps can be useful, as they can be easily adjusted and repositioned as needed.
- Heavy-Duty Applications: In heavy-duty applications, such as industrial piping or construction, choose clamps with high clamping forces and rugged designs to withstand demanding environments.
Tips for Selection:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for clamp capacity and load ratings.
- Consider the working environment (e.g., temperature, moisture, chemicals) and choose clamps made from materials that can withstand those conditions.
- For critical applications, consider using multiple clamps or additional support mechanisms for added safety and stability.
- Invest in high-quality clamps from reputable manufacturers to ensure durability and reliable performance.
By considering these factors and matching the clamp to your specific application, you can ensure a secure and safe clamping solution for your pipe-related tasks.
Pipe Clamp Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care are essential for extending the lifespan of your pipe clamps and ensuring their continued safe and efficient operation. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and proper storage can help prevent premature wear, rust, and other issues that could compromise the clamp’s performance.
Cleaning
Pipe clamps are often exposed to various jobsite conditions, including dirt, debris, and other contaminants. It’s crucial to clean your clamps after each use to prevent the buildup of grime, rust, and other materials that could interfere with their functionality. Use a wire brush or a mild degreaser to remove any stubborn dirt or grime, and then wipe the clamps clean with a dry cloth.
Lubrication
Lubrication is essential for maintaining the smooth operation of pipe clamps. Over time, the moving parts can become dry and stiff, making it difficult to adjust or tighten the clamp. Use a high-quality lubricant designed for metal-on-metal applications, such as a dry lubricant or a light machine oil. Apply a small amount of lubricant to the threaded rod, pivot points, and any other moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
Storage
Proper storage is crucial for preventing damage and extending the lifespan of your pipe clamps. Store your clamps in a dry, clean environment, away from moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct sunlight. Consider using a storage cabinet or a tool chest to protect your clamps from dust and debris. If storing clamps for an extended period, apply a light coat of rust-preventative oil to protect the metal surfaces.
Extending Lifespan
In addition to regular maintenance, there are several steps you can take to extend the lifespan of your pipe clamps:
- Avoid overloading: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended load limits and never exceed the clamp’s capacity. Overloading can cause permanent deformation or damage to the clamp.
- Use appropriate clamp sizes: Ensure that you are using the correct clamp size for the job. Using an undersized clamp can lead to excessive stress and premature wear.
- Inspect regularly: Regularly inspect your pipe clamps for signs of wear, cracks, or other damage. Replace any clamps that show significant wear or damage to prevent potential failures.
- Handle with care: Avoid dropping or subjecting your pipe clamps to excessive impact, as this can cause internal damage or deformation.
By following these maintenance and care guidelines, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your pipe clamps, ensuring that they remain reliable and effective tools for years to come.
Pipe Clamp Safety
Pipe clamps are essential tools for various applications, but they can pose significant safety risks if not used properly. Proper handling, awareness of pinch points, adhering to load limits, and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) are crucial for ensuring safe operations with pipe clamps.
Proper Handling: Always ensure that pipe clamps are securely tightened and properly positioned before applying any load. Avoid using excessive force when tightening the clamps, as this can damage the clamp or the workpiece. Never place your hands or fingers between the jaws of the clamp and the workpiece during tightening or loosening.
Pinch Points: Pipe clamps have several pinch points where fingers or hands can become trapped or crushed. Be extremely cautious when operating the clamp, and keep your hands and fingers away from these pinch points. Wear gloves to provide additional protection against pinching hazards.
Load Limits: Every pipe clamp has a maximum load capacity specified by the manufacturer. Exceeding this load limit can cause the clamp to fail, potentially leading to serious injuries or damage to the workpiece. Always check the load capacity and ensure that the clamp is appropriate for the intended application.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Depending on the specific task and work environment, wearing appropriate PPE is essential when using pipe clamps. Safety glasses or goggles can protect your eyes from flying debris or sparks, while gloves can prevent cuts and pinching injuries. In some cases, steel-toed boots, hard hats, or other protective gear may be necessary.
By following these safety guidelines and exercising caution when using pipe clamps, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Remember, your safety should always be the top priority when working with any tools or equipment.
Pipe Clamp Accessories and Attachments
Pipe clamps can be enhanced with various accessories and attachments to improve their versatility, functionality, and performance. These add-ons cater to different clamping needs and material surfaces, ensuring a secure grip and preventing damage to the workpieces.
Clamp Pads
Clamp pads are essential accessories that protect delicate or finished surfaces from being marred or scratched by the clamp jaws. They are typically made of soft materials like rubber, plastic, or leather, and are designed to fit snugly over the clamp jaws. Clamp pads not only safeguard the workpiece but also provide additional friction, preventing slippage during clamping.
Jaw Covers
Similar to clamp pads, jaw covers are protective sleeves that slide over the clamp jaws. They are often made of durable materials like nylon or polyurethane, offering a longer-lasting solution for clamping rough or abrasive surfaces. Jaw covers can be particularly useful when working with materials that may damage or wear down the clamp jaws over time.
Extensions
Pipe clamp extensions are cylindrical rods that can be attached to the clamp’s spindle, effectively increasing its reach and clamping capacity. These extensions are ideal for clamping larger workpieces or accessing hard-to-reach areas. They come in various lengths and diameters to accommodate different clamping requirements.
Swivel Attachments
Swivel attachments, also known as swivel pads or swivel heads, are versatile accessories that allow the clamp jaws to pivot and rotate. This feature is particularly useful when clamping irregularly shaped or angled workpieces, as it enables the jaws to conform to the surface contours. Swivel attachments can be either permanently attached to the clamp or designed as removable accessories.
These accessories and attachments not only enhance the functionality of pipe clamps but also contribute to their versatility, making them adaptable to a wide range of clamping tasks and material types. By choosing the right accessories, users can optimize their clamping setup, improve efficiency, and achieve better results in their projects.
Pipe Clamps in Professional Settings
Pipe clamps are essential tools in various professional settings, particularly in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive repair. Their versatility and strength make them invaluable for securing pipes, tubing, and other materials during assembly, maintenance, and repair operations.
Industrial Uses:
In industrial environments, pipe clamps are used extensively for holding pipes and tubing in place during welding, cutting, or fitting processes. They provide a secure grip, ensuring the stability and alignment of the components being worked on. Pipe clamps are particularly useful in factories, power plants, and other industrial facilities where precise pipe work is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of machinery and equipment.
Construction Sites:
On construction sites, pipe clamps play a vital role in plumbing and HVAC installations. They are used to hold pipes in position while connecting them or making adjustments. Pipe clamps are essential for ensuring proper alignment and preventing leaks or other issues that could compromise the integrity of the plumbing or HVAC system.
Automotive Repair:
In the automotive industry, pipe clamps are widely used for holding fuel lines, brake lines, and other types of tubing in place during repair or replacement procedures. They provide a secure grip, preventing the lines from shifting or becoming dislodged during the work process. Pipe clamps are particularly useful when working on engines, transmissions, and other intricate components where space is limited and precise positioning is critical.
Regardless of the professional setting, pipe clamps are designed to withstand heavy loads and provide a reliable hold on pipes and tubing. They are often made from durable materials such as steel or aluminum alloys to ensure long-lasting performance and resistance to wear and tear. Many pipe clamps feature adjustable mechanisms that allow them to accommodate a range of pipe sizes, making them versatile tools for various applications.
History and Evolution of Pipe Clamps
Pipe clamps have a rich history that can be traced back to the early days of plumbing and construction. The origins of these versatile tools can be attributed to the need for secure and reliable methods of joining pipes during the installation and repair of plumbing systems.
Origins
The earliest forms of pipe clamps were simple devices made from wood or metal, designed to hold pipes in place temporarily during assembly or maintenance tasks. As the demand for more efficient and durable plumbing systems grew, so did the need for improved pipe clamping solutions.
Design Improvements
Over time, pipe clamps underwent significant design improvements, incorporating features such as adjustable jaws, quick-release mechanisms, and more robust materials. These advancements allowed for easier installation, increased clamping force, and better adaptability to various pipe sizes and materials.
One notable development was the introduction of chain pipe clamps, which offered greater flexibility and the ability to clamp pipes at different angles and orientations. This innovation was particularly useful in situations where traditional straight clamps were not practical or effective.
Modern Advancements
In recent years, pipe clamps have continued to evolve, benefiting from advances in materials science and manufacturing technologies. Modern pipe clamps are often made from lightweight yet strong materials like aluminum alloys or high-strength polymers, ensuring durability and corrosion resistance.
Additionally, ergonomic designs and improved grip surfaces have made pipe clamps more user-friendly and safer to operate, reducing the risk of slippage or injury during use.
Technological advancements have also led to the development of specialized pipe clamps for specific applications, such as those used in the automotive, aerospace, and heavy industries, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Overall, the history and evolution of pipe clamps reflect the ingenuity and problem-solving skills of engineers and tradespeople, who have continuously sought to improve these essential tools to meet the ever-changing demands of modern construction and plumbing projects.
Pipe Clamp Brands and Manufacturers
The pipe clamp market is dominated by a handful of industry-leading brands that have established themselves as reliable and trusted manufacturers. These brands offer a wide range of pipe clamps, catering to various industries and applications.
One of the most well-known brands in the pipe clamp industry is RIDGID. Known for their durable and high-quality products, RIDGID offers a comprehensive line of pipe clamps, from lightweight aluminum models to heavy-duty cast iron clamps. Their products are favored by professionals in the plumbing, construction, and manufacturing industries for their durability and ease of use.
Another top brand is Pony. Pony has been manufacturing pipe clamps for over 60 years and is renowned for their innovative designs and attention to detail. Their clamps are available in various materials, including steel, aluminum, and cast iron, and are designed to provide maximum clamping force and stability.
Bessey is another prominent name in the pipe clamp market. This German company is known for its precision-engineered products and commitment to quality. Bessey’s pipe clamps are designed for both professional and DIY applications, offering a range of sizes and styles to suit different needs.
When it comes to affordability and value, brands like Irwin and Jorgensen offer high-quality pipe clamps at competitive prices. These brands have established themselves as reliable options for those seeking a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness.
In terms of industry leaders, brands like RIDGID, Pony, and Bessey stand out for their reputation, quality, and innovation. However, it’s important to note that the choice of brand often comes down to personal preference, specific application requirements, and budget considerations.
When selecting a pipe clamp brand, it’s essential to consider factors such as clamp capacity, material quality, ease of use, and durability. Many manufacturers provide detailed specifications and user reviews, which can help in making an informed decision.
Pipe Clamp Alternatives and Substitutes
While pipe clamps are versatile and widely used, there are several alternatives and substitutes available depending on the specific application and budget constraints.
Other Clamping Tools
For smaller projects or when working with different materials, other clamping tools such as C-clamps, bar clamps, corner clamps, or spring clamps can be used instead of pipe clamps. These tools offer different clamping mechanisms and may be more suitable for certain tasks.
Improvised Solutions
In some situations, improvised solutions can be employed as a cost-effective alternative to pipe clamps. For example, using ratchet straps, rope, or even bungee cords can provide temporary clamping force. However, these solutions may not offer the same level of precision and stability as dedicated pipe clamps.
Cost-effective Options
For those on a tight budget or working on smaller projects, there are cost-effective options available. These may include budget-friendly pipe clamp alternatives made from materials like plastic or aluminum, which can provide adequate clamping force for lighter-duty applications.
It’s important to note that while alternatives and substitutes can be useful in certain situations, they may not offer the same level of performance, durability, or versatility as high-quality pipe clamps. Carefully evaluate the project requirements and choose the most suitable option based on factors such as clamping force needed, material compatibility, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Future of Pipe Clamps
The future of pipe clamps is poised for exciting advancements driven by emerging technologies, design innovations, and industry trends. As the demand for efficient and versatile clamping solutions continues to grow, manufacturers are exploring new materials, ergonomic designs, and smart features to enhance the functionality and user experience of pipe clamps.
One significant trend is the integration of digital technologies into pipe clamps. Smart pipe clamps equipped with sensors and connectivity capabilities could provide real-time data on clamping force, pressure, and alignment, enabling precise adjustments and ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, the incorporation of augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR) technologies could revolutionize the way pipe clamps are used, offering virtual guidance and training for proper installation and operation.
Advancements in materials science are also shaping the future of pipe clamps. Manufacturers are exploring the use of lightweight yet strong composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, to create durable and corrosion-resistant pipe clamps. These materials could offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, making pipe clamps more portable and easier to maneuver, especially in confined spaces.
Design innovations are focused on improving ergonomics and user-friendliness. Pipe clamps with adjustable handles, anti-slip grips, and intuitive locking mechanisms could reduce strain and fatigue, enhancing safety and productivity on job sites. Additionally, modular and reconfigurable designs may allow for greater versatility, enabling pipe clamps to adapt to various pipe sizes and configurations without the need for multiple specialized tools.
Sustainability is another driving force in the future of pipe clamps. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes to reduce the environmental impact of pipe clamps throughout their lifecycle. This includes the use of recycled or renewable materials, as well as the development of reusable and easily repairable pipe clamps, promoting a circular economy approach.
Furthermore, the rise of additive manufacturing (3D printing) could revolutionize the production and customization of pipe clamps. This technology could enable on-demand manufacturing of specialized pipe clamps tailored to specific project requirements, reducing lead times and minimizing inventory costs.
As the construction, plumbing, and manufacturing industries continue to evolve, the future of pipe clamps will be shaped by ongoing research, innovation, and a commitment to meeting the ever-changing needs of professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.



